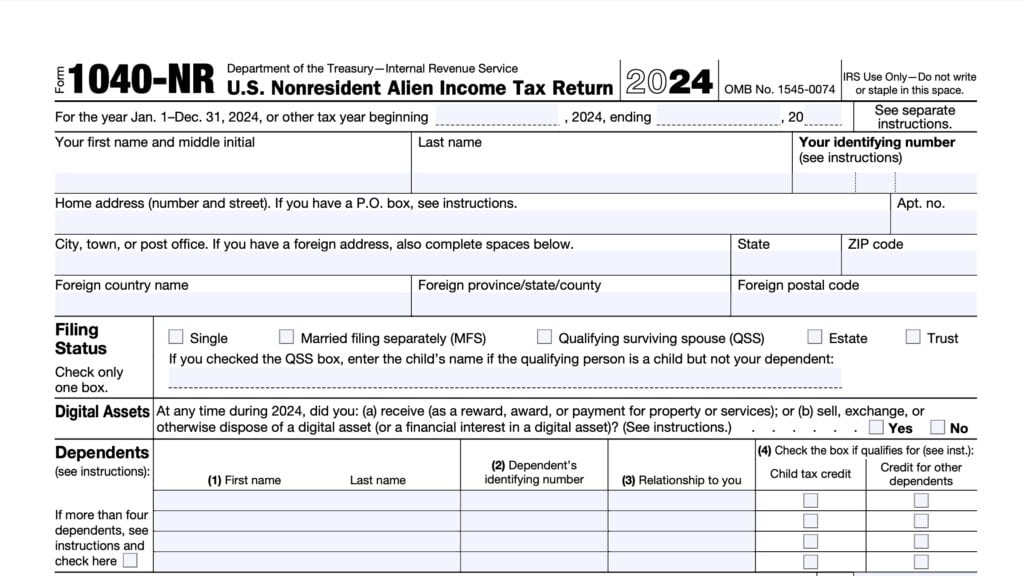
Schedule NEC Instructions (Form 1040-NR)
If you’re a nonresident reporting items of income to the U.S. Internal Revenue Service on your Form 1040-NR, you may need to complete Schedule NEC, Tax on Income Not Effectively Connected With a U.S. Trade or Business.
In this article, we’ll walk through everything you need to know about Schedule NEC, including how to:
- Complete Schedule NEC
- Calculate your tax liability on Schedule NEC items of income
- Determine which items to report on Schedule NEC and which items to report elsewhere
Let’s start with a walk through of this one-page tax form.
Contents
Table of contents
How do I complete IRS Schedule NEC?
We’ve broken down this one-page tax schedule into three parts:
Let’s start at the top with the taxpayer information fields.
Taxpayer information

Nature of Income
Before reporting items of income on Schedule NEC, there are two key points to understand:
- Distinguishing between:
- Income that is effectively connected with a U.S. Trade or Business, and
- Income not effectively connected with a U.S. Trade or Business
- How to calculate the appropriate tax rate for each item of income.
We provide further explanation on each of these topics in Filing Considerations, below.
Taxpayers use Schedule NEC specifically to report items of income not effectively connected with a U.S. Trade or Business. Also, taxpayers are responsible for calculating their applicable tax rate based upon existing tax law and the applicable tax treaty.
For reference, you can find a list of current U.S. tax treaties on the Internal Revenue Service website.
For Schedule NEC, we will focus exclusively on how to report items of income that are not effectively connected with a U.S. Trade or Business. We will also assume that you are able to calculate your own applicable tax rate for each item of income.
Need assistance?
Do you need help determining whether an item of income is connected with U.S. Trade or Business? Do you need help understanding how a U.S. tax treaty might apply to you?
If so, schedule a one-on-one appointment today! For a nominal fee, you can discuss your tax questions with me. Click here to get started!
Lines 1 through 15
For Lines 1 through 15, you must separately determine whether your item of income is subject to tax at one of the following tax rates:
- Column (a): 10%
- Column (b): 15%
- Column (c): 30%
- Column (d): Other (specify, based upon the terms of your particular tax treaty)
Generally, tax must be withheld at the source on income not effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business that is paid to nonresident aliens. The withholding rate is generally at a 30% rate, and must be withheld by the person who pays the income.
However, the tax withholding tax rate may be lower or the income may be exempt if your country of tax residence and the United States have a treaty setting lower rates
Once calculated under the correct tax rate, enter each item of income under the appropriate column on each line.
Line 1: Dividends and dividend equivalents
This is broken down into three types of dividend income.
Line 1a: Dividends paid by U.S. corporations
Unless otherwise indicated, include all dividends paid by U.S. corporations on Line 1a.
Line 1b: Dividends paid by foreign corporations
Include all U.S. source dividends paid by foreign corporations on Line 1b.
Line 1c: Dividend equivalent payments with respect to Section 871(m) transactions
Include all dividend equivalent payments received with respect to Internal Revenue Code Section 871(m) transactions here.
Dividend equivalent payments
Dividend equivalent payments include the following.
- Substitute dividends paid pursuant to:
- A securities lending transaction,
- A sale-repurchase transaction, or
- Substantially similar transaction;
- A payment that references a U.S. source dividend made pursuant to a specified notional principal contract (NPC); or
- A payment that references a U.S. source dividend made pursuant to a specified equity-linked instrument (ELI).
Exceptions
The following items of dividend income that you received as a nonresident alien are generally exempt from the 30% tax.
- Interest-related dividends received from a mutual fund.
- Short-term capital gain dividends from a mutual fund only if you were present in the United States for less than 183 days during the tax year.
- The part of the dividend attributable to the foreign gross income if a U.S. corporation in existence beginning before January 1, 2011:
- Received 80% of its gross income from the active conduct of a foreign business, and
- Continues to receive 80% of its gross income from the active conduct of a foreign business,
- U.S. source dividends paid by certain foreign corporations.
Line 2: Interest
Include interest items under the applicable line.
Line 2a: Mortgage interest
This line includes mortgage interest paid to you.
Line 2b: Interest paid by foreign corporations
Include interest income paid by other foreign corporations in Line 2b.
Line 2c: Other interest
Line 2c includes other interest not covered by Lines 2a or 2b.
Exceptions
The following items of interest income that you received as a nonresident alien are generally exempt from the 30% tax.
- Interest from a U.S. bank, savings and loan association, or similar institution, and from certain deposits with U.S. insurance companies.
- Portfolio interest on obligations issued after July 18, 1984.
- Interest on any tax-exempt original issue discount (OID) such as state or local bonds.
Line 3: Industrial royalties (patents, trademarks, etc.)
Enter royalty income related to patents, trademarks, or other industry-related intellectual property in Line 3.
Line 4: Motion picture or TV copyright royalties
In Line 4, enter copyright royalties related to movies or television programming.
Line 5: Other royalties (copyrights, recording, publishing, etc.)
In Line 5, enter other royalty income received from:
- Copyrights
- Recording rights
- Publishing rights
- Other similar types of royalties not covered in another line
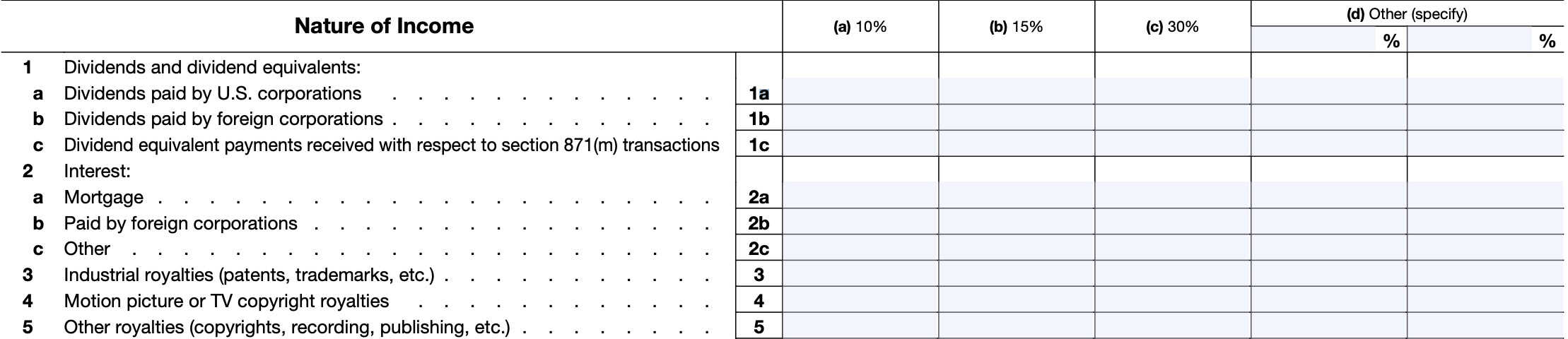
Line 6: Real property income and natural resources royalties
Enter income from real property on Line 6.
However, do not include any income that you elected to treat as effectively connected and included on Schedule 1 (Form 1040), Line 5.
Line 7: Pensions and annuities
Enter pension income or annuity income that was not effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business.
Report pensions and annuities that are effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business on IRS Form 1040-NR, Lines 5a and 5b
Line 8: Social Security benefits
Enter any Social Security benefits you received in Line 8.
Social Security benefits taxation
85% of the U.S. social security and equivalent railroad retirement benefits you received are taxable. This amount is treated as U.S. source income not effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business. It is subject to the 30% tax rate, unless exempt or taxed at a reduced rate under a U.S. tax treaty.
Social security benefits include:
- Any monthly benefit under Title II of the Social Security Act or
- The part of a tier 1 railroad retirement benefit treated as a social security benefit.
They don’t include any Supplemental Security Income (SSI) payments. SSI payments are not considered taxable income.
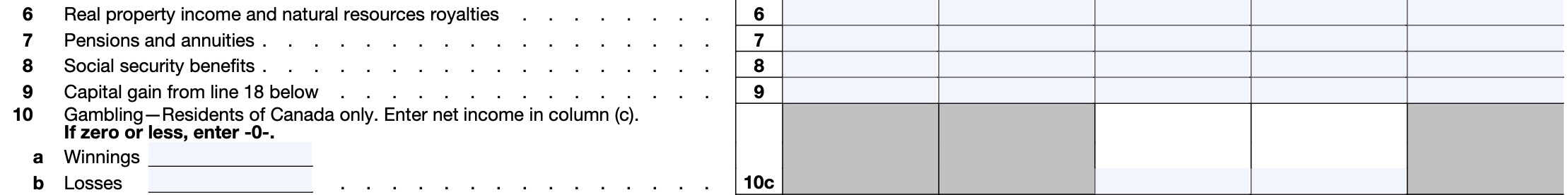
Line 9: Capital gain from Line 18 below
Enter the capital gain calculated on Line 18, later in this form.
Line 10: Gambling (For residents of canada only)
Line 10 is for Canadian residents only. All other taxpayers reporting gambling winnings should report them on Line 11, below.
Line 10a: Winnings
If you’re a resident of Canada who is not engaged in the trade or business of gambling, enter all gambling winnings on Line 10a. Include proceeds from lotteries and raffles.
Do not include winnings from any of the following:
- Blackjack
- Baccarat
- Craps
- Roulette
- Big-6 wheel
You can deduct your U.S. source gambling losses to the extent of your U.S. source gambling winnings.
Line 10b: Losses
Enter gambling losses on Line 10b.
Line 10c: Net income
Subtract Line 10b from Line 10a. If this results in 0 or a negative number, enter ‘0.’ A net loss from gambling activities is not deductible.
Line 11: Gambling (Residents of countries other than canada)
If you aren’t engaged in the trade or business of gambling and are a resident of a country that has a tax treaty with the United States, you may be exempt by treaty from paying tax on gambling winnings.
Exempt from paying tax
If your gambling winnings are exempt by treaty, enter all gambling winnings on Line 11, column (d), specifying 0%. However, you must know the terms of the tax treaty between the United States and the country of which you claim to be a resident to properly claim an exemption from withholding.
Not exempt from paying tax
If you aren’t engaged in the trade or business of gambling and are a resident of a country without a tax treaty with the United States or a resident of a country with a tax treaty that doesn’t provide a reduced rate of, or exemption from, withholding for gambling winnings, then enter all gambling winnings on Line 11, column (c).
Include proceeds from lotteries and raffles.
Do not include winnings from any of the following:
- Blackjack
- Baccarat
- Craps
- Roulette
- Big-6 wheel
You can’t offset losses against winnings and report the difference unless the winnings and losses are from the same session
If you have winnings from blackjack, baccarat, craps, roulette, or big-6 wheel, and the casino gave you a Form 1042-S showing that tax was withheld, enter these winnings on line 11, column (d), and enter 0% as the tax rate. You can claim a refund of the tax.

Line 12: Other
Include all U.S. source income that hasn’t been reported on another line or isn’t excluded from tax. This might include the following:
- Certain alimony payments you received
- Generally, alimony payments received from a divorce that was finalized on or before December 31, 2018 are considered taxable income
- Prizes and awards
- Tax withheld pursuant to Section 5000C on specified federal procurement payments
- Taxable distributions from an ABLE account.
- Certain gains from the sale or exchange of any personal property
Certain gains from the sale or exchange of personal property are taxable regardless if you received a Form 1099-K for the transaction(s). IRS Publication 519, U.S. Tax Guide for Aliens, contains additional information.
Line 13
Add Lines 1a through 12 for each column. Enter the totals for each column in Line 13.
Line 14
Multiply each number in Line 13 by the tax rate at the top of the respective column. Enter the product of each calculation in Line 14.
Line 15: Tax on income not effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business
Add the totals of each item in Line 14. This represents the total tax on income not effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business.
Enter this number on your Form 1040-NR, Line 23a.
Capital Gains and Losses from Sales or Exchanges of Property
In this section, we’ll calculate the total capital gain or losses from property sales or exchanges that are
- From sources within the United States, and
- Not effectively connected with a U.S. business
Do not include a gain or loss disposing of interest in U.S. real property (real estate). Report these on Schedule D (Form 1040). You may also need to use IRS Form 4797, Sales of Business Property, depending on the nature of the transaction.
Additionally, if you have capital gains and losses from the sales or exchanges of property, consider the following:
- Include these gains and losses only if you were in the United States at least 183 days during 2024.
- Gains or losses aren’t subject to U.S. tax if you were in the United States less than 183 days during the tax year.
- In determining your net gain, don’t use the capital loss carryover.
- The IRS does not allow you to deduct losses from sales or exchanges of capital assets in excess of gains.
- You may need to report certain transactions on Schedule P (Form 1040-NR) if you transferred an interest in a partnership that
- Is either directly or indirectly engaged in the conduct of a trade or business within the United States, or
- Holds any U.S. real property interests
Line 16
Enter any applicable transactions in Line 16. Specific instructions for each column are below.
Line 16(a): Kind of property and description
Enter the type of property and a description. If required, attach a statement containing additional details about the property.
Line 16(b): Date acquired
Enter the date you acquired the property. Use the conventional U.S. format: MM/DD/YYYY
Note: Many non-U.S. citizens may be familiar with this dating convention: DD/MM/YYYY. Please note that using this convention on U.S. tax forms might cause tax errors.
For example, calculations that might otherwise result in long-term capital gains tax treatment (preferred tax rates) may be confused as short-term capital gains, and vice versa.
Line 16(c): Date sold
Enter the date you sold or disposed of the property.
Line 16(d): Sales price
In Line 16(d), enter the sales price.
Line 16(e): Cost or other basis
Enter the cost or other basis for the property you disposed of.
Line 16(f): Loss
If Line 16(e) is more than Line 16(d), you have a loss. Subtract Line 16(d) from Line 16(e) and enter the difference here.
Line 16(g): Gain
If Line 16(d) is more than Line 16(e), you have a gain. Subtract Line 16(e) from Line 16(d) and enter the difference here.
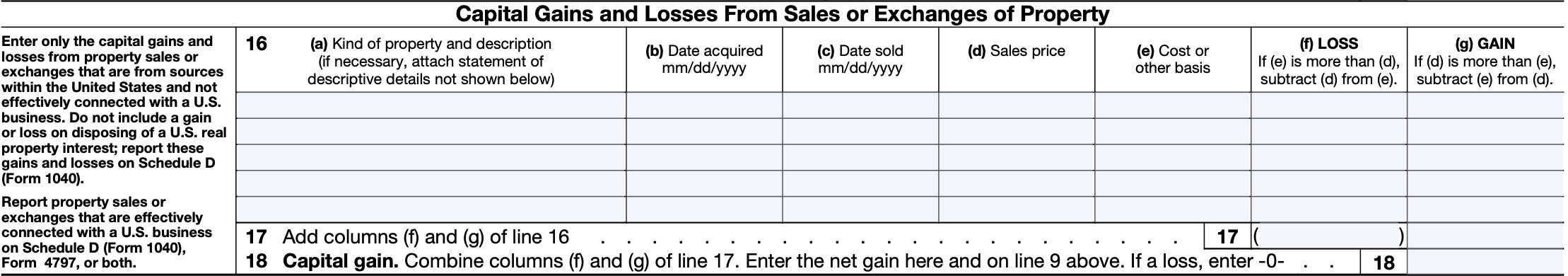
Line 17
Add columns (f) and (g) of all items entered in Line 16. Enter the sum of each into the respective column on Line 17.
Line 18
Combine Line 17(f) and Line 17(g). Enter the net gain here and on Line 9.
Filing considerations
There are a couple of filing considerations worth discussing here:
- Distinguishing between income that is effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business (ECI), and income not effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business
- How to calculate the appropriate tax rate for each item of income
Distinguishing income
On Schedule NEC, you should include income only to the extent it’s U.S. source and not effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business in the United States.
These income items are generally subject to a 30% tax rate and will be withheld at a 30% withholding rate. However, your tax treaty may
The form instructions contain the following examples of categories of noneffectively connected income:
- Income that is fixed or periodic, such as:
- Interest income
- Dividends
- Rental income
- Salaries and wages
- Premiums
- Annuity income
- Other compensation
- Certain U.S. source alimony
- From divorces finalized on or before December 31, 2018
- Gains, other than capital gains, from the sale or exchange of patents, copyrights, and other intangible property.
- Original issue discount (OID). If you sold or exchanged the obligation, include the OID that
accrued while you held the obligation minus the amount previously included in income. - Capital gains in excess of capital losses from U.S. sources during 2024.
- Include these gains only if you were in the United States at least 183 days during 2024.
- Prizes, awards, and certain gambling winnings.
Publication 519, U.S. Tax Guide for Aliens, and the IRS page on Effectively Connected Income both contain additional information on determining ECI.
Calculating an appropriate tax rate
The IRS instructions for Schedule NEC state: Tax must be withheld at the source on income not effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business that is paid to nonresident aliens. The withholding is generally at a 30% rate. The tax must be withheld by the person who pays the income.
However, your tax treaty may determine a different tax rate on certain types of income. It is considered the taxpayer’s responsibility to calculate this tax rate and properly report it on Schedule NEC.
Video walkthrough
Learn more about completing Schedule NEC in this step-by-step video:
Frequently asked questions
Nonresident aliens use Schedule NEC to calculate and report tax on income not effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business. Taxes calculated on Schedule NEC are reported on Line 23a of Form 1040-NR.
Taxpayers generally should file Schedule NEC with the rest of their Form 1040-NR.
Schedule NEC is due on the same date as IRS Form 1040-NR.