IRS Form 2848 Instructions
If the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) decides to investigate your income tax return, you may need to use an IRS power of attorney form, to appoint a qualified representative. This form is known as IRS Form 2848, Power of Attorney and Declaration of Representative.
In this article, we’ll walk through everything you need to know about IRS Form 2848, including:
- How to complete and file IRS Form 2848
- Appropriate uses for IRS Form 2848
- Frequently asked questions
Let’s begin with a top-down overview of this tax form.
Table of contents
How do I complete IRS Form 2848?
There are two parts to this form:
Let’s take a closer look by starting at the top of Part I.
Part I: Power of Attorney
This section contains the information about the powers delegated to the representative. Before we go through each line, it’s important to note that each taxpayer must complete separate forms. In other words, a tax professional cannot have a blanket grant of authority on behalf of multiple taxpayers.
Line 1: Taxpayer information
Line 1 contains the taxpayer’s information. This includes:
- Taxpayer’s name and address
- Taxpayer identification number (TIN):
- Social Security number (SSN)
- Employer identification number (EIN)
- Individual taxpayer identification number (ITIN)
- Daytime phone number
- Plan number, if applicable.
- Applies primarily to employee plans
If you have recently changed your address
The IRS instructions point out that simply providing your new address will not update your IRS records. Instead, you should use one of the following IRS change of address forms to do so:
If you would like to learn more about using IRS Form 8822 to update your address, watch this step by step video.
Individuals
Individual taxpayers who operate a sole proprietorship and file their business tax return on Schedule C should enter both of the following:
- Social Security number or ITIN, whichever is applicable
- Employer identification number
If you do not already have one, you may file Form SS-4 to apply for an employer identification number.
Exempt organizations
Enter the name, address, and EIN of the tax-exempt organization.
Estates
Enter the name of the decedent and the name, title, and address of the decedent’s executor or personal representative.
For Forms 706, enter the decedent’s SSN (or ITIN) for the taxpayer identification number.
For all other IRS forms, enter the estate’s EIN for the taxpayer identification number. If the estate does not have an EIN, enter the decedent’s SSN (or ITIN).
Trusts
Enter the name, title, and address of the trustee, and the name and EIN of the trust.
Deceased taxpayers
Enter the name and SSN (or ITIN) of the decedent and the name, title, and address of the decedent’s executor or personal representative.
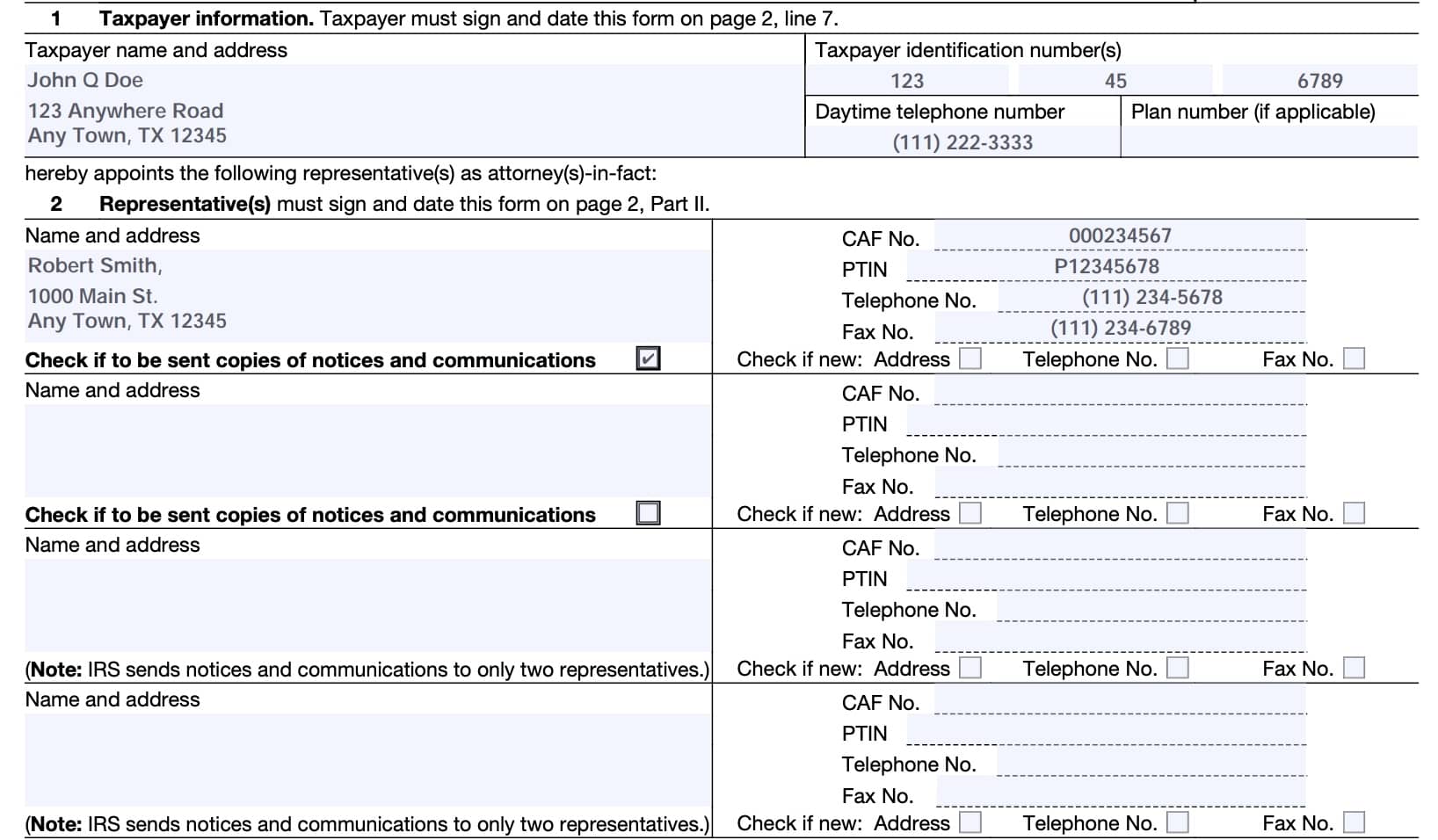
Line 2: Representative(s)
This form allows up to 4 chosen representatives. For each designated representative, include the following information:
- Name and address
- CAF Number
- Preparer Tax Identification Number (PTIN)
- Telephone Number
- Fax number
Also, check the appropriate box if there is a new address, telephone number, or fax number. Additionally, the taxpayer may check a box to allow the IRS to send notices and communication for up to two designated representatives.
Line 3: Acts authorized
In order for the power of attorney document to be valid, you must enter the following information:
- Description of the matter (i.e. type of tax)
- Tax form number (where applicable), and
- Year(s) or period(s) where applicable
As outlined in the below example, a taxpayer may list:
- Description of matter: Income tax
- Form: IRS Form 1040
- Year(s) or period(s): Calendar years 2022 through 2026
Under periods, a taxpayer may list consecutive multiple years, or a series of inclusive periods, like:
- 2018 through 2020
- 2nd 2018-3rd 2019
Representation only applies for the periods listed on Line 3, and only the tax forms directly related to the listed taxpayer.
Although a taxpayer may list future tax years or periods, the IRS will not record future tax years or periods that exceed 3 years from December 31 of the tax year that the IRS receives the power of attorney form. In other words, you cannot create a permanent authorization for your representative with this filing.
Married couples filing a joint return
Married couples filing jointly must execute their own separate Form 2848.
Innocent spouse relief
If you would like your authorized individual to assist you with requesting innocent spouse relief, you must specify this. To do so, you would enter the following:
- Description of matter: Innocent Spouse Relief
- Form: IRS Form 8857
- Year(s) or period(s): Enter the year (or years) impacted
If you describe innocent spouse relief on Line 3, your representative may sign IRS Form 8857 for you requesting innocent spouse relief.
If you do not describe innocent spouse relief on Line 3, and your innocent spouse relief form is attached to IRS Form 2848, you must sign IRS Form 8857; your representative may not sign the form for you.
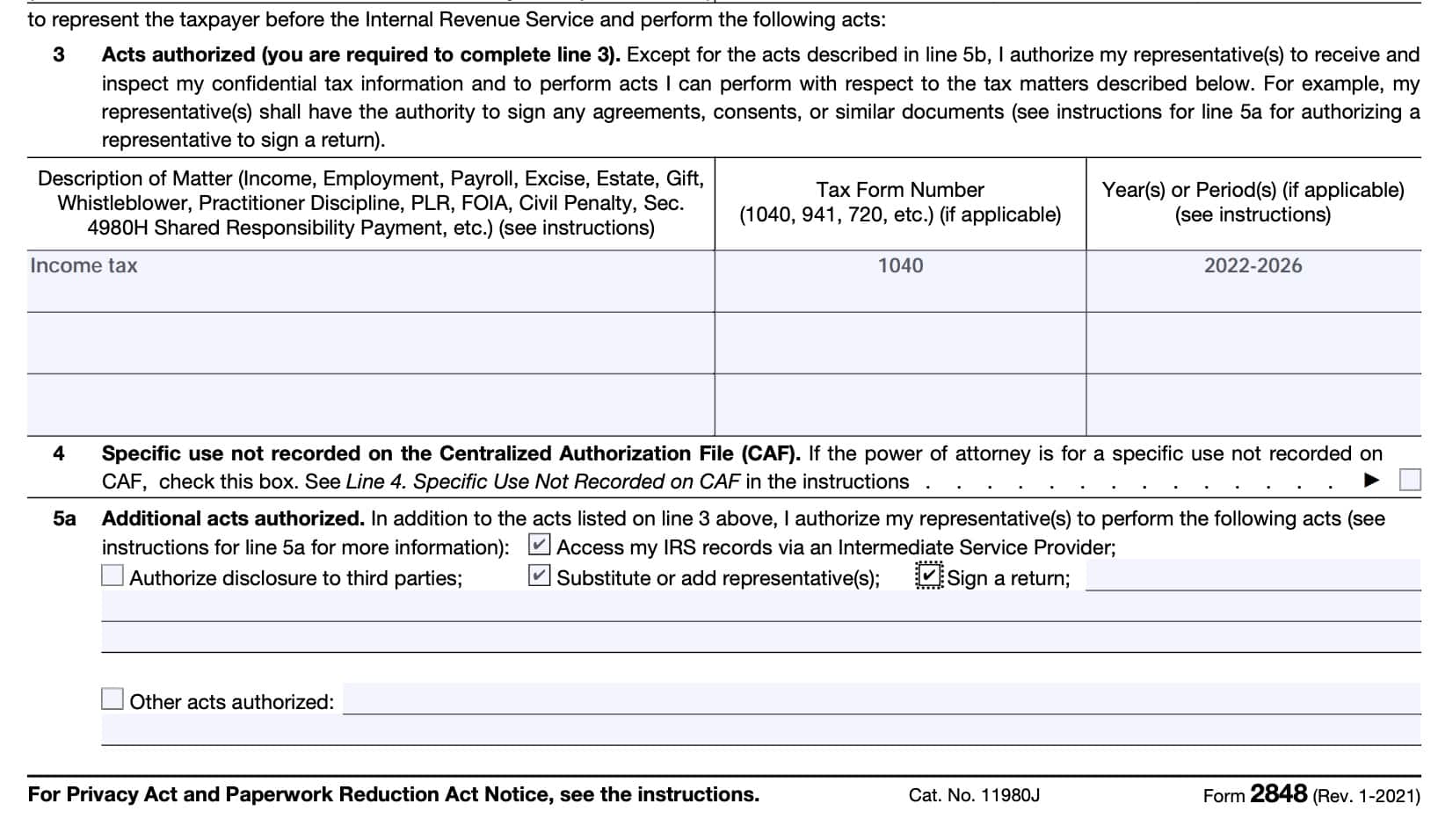
Line 4: Specific use not recorded on the Centralized Authorization File (CAF)
There may be specific, one-time reasons to authorize a power of attorney, in a limited situation. These acts are not recorded on the CAF.
Examples include:
- Requests for a private letter ruling or technical advice.
- See Rev. Proc. 2021-1 for additional information
- Applications for an EIN
- Claims filed on IRS Form 843, Claim for Refund and Request for Abatement
- Corporate dissolutions filed on IRS Form 966
- Circular 230 disciplinary investigations and proceedings
- Requests to change accounting methods or periods
- Applications for recognition of exemption under IRC sections 501(c)(3), 501(a), or 521 (Forms 1023, 1024, or 1028)
- Request for a determination of the qualified status of an employee benefit plan (Forms 5300, 5307, 5316, or 5310)
- Applications for an ITIN filed on Form W-7, Application for IRS Individual Taxpayer Identification Number
- Applications for an exemption from self-employment tax filed on IRS Form 4361, Application for Exemption From Self-Employment Tax for Use by Ministers, Members of Religious Orders and Christian Science Practitioners
- Filing IRS Form 211, Application for Award for Original Information under IRC Section 7623 (whistleblower law)
- Voluntary submissions under the Employee Plans Compliance Resolution System (EPCRS) and
- Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) requests.
Check the box on Line 4 if the power of attorney is for a specific issue or specific tax matters that the IRS will not record on the CAF. Checking this box will not revoke the original power of attorney, if one is already recorded on the CAF system.
If you check the box on Line 4, the representative should mail or fax the power of attorney to the IRS office handling the matter. Otherwise, the representative should bring a copy of the completed Form 2848 to each meeting with the IRS.
Line 5a: Additional acts authorized
In this part, a taxpayer may select additional acts that they choose to authorize for their representative. This includes:
- Accessing taxpayer’s IRS records through an Intermediate Service Provider (ISP)
- If you do not authorize the use of an Intermediate Service Provider, your representative can obtain your tax information directly from the IRS by using the IRS e-Services Transcript Delivery System
- Authorized disclosure to third parties
- Substitute or adding representatives
- Signing a return
- Per Treasury Regulations Section 1.6012-1(a)(5), only authorized if the taxpayer is sick or injured, continuously out of the United States, or specific permission is granted by the IRS
- Other specific acts
Line 5b: Specific acts not authorized.
Conversely, a taxpayer may specify any act in which the authorized power of attorney does not have the taxpayer’s express permission to perform. To make this selection, the taxpayer simply needs to write in specific acts that they wish to exclude from their representative’s authority.
Regardless of what the taxpayer may enter in Line 5b, under no circumstances may an authorized representative:
- Endorse or negotiate a check on behalf of a taxpayer
- Accept payment or direct payment into an account owned or controlled by the representative or associated entity
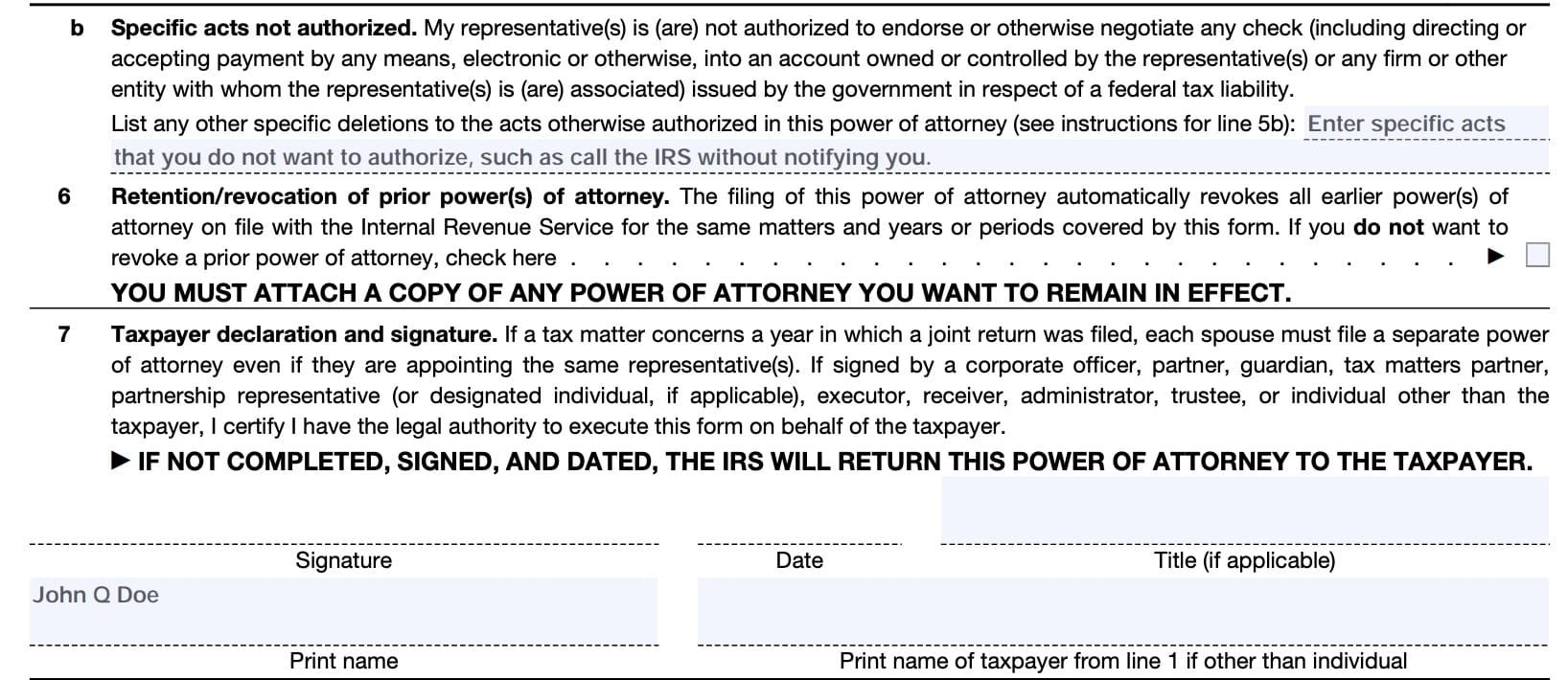
Line 6: Retention/Revocation of Prior Power(s) of Attorney
Unless otherwise directed, filing Form 2848 nullifies other power of attorney forms on file for the same tax-related matters, years, or periods covered by this form.
If there is a power of attorney the taxpayer does not want to revoke, the taxpayer must:
- Check the box in Line 6, and
- Attach a copy of the power of attorney to remain in effect
If you file IRS Form 2848, this will not nullify any IRS Form 8821, Tax Information Authorization, that might be in effect.
Line 7: Taxpayer declaration and signature
This field includes the taxpayer printed name, date, and signature.
You must handwrite your signature on Form 2848 if you file it by mail or by fax. Digital, electronic, or typed-font signatures are not valid signatures for Forms 2848 filed by mail or by fax.
If you choose to use an electronic signature, then you must file Form 2848 online through the IRS website.
Part II: Declaration of Representative
Part II contains a declaration of the taxpayer’s representative that he or she meets the IRS criteria for representation.
Each representative will enter:
- The corresponding letter (a-r) of their qualification
- Licensing jurisdiction or authority
- Bar, license, certification, registration, or enrollment number (if applicable)
- Signature
- Date
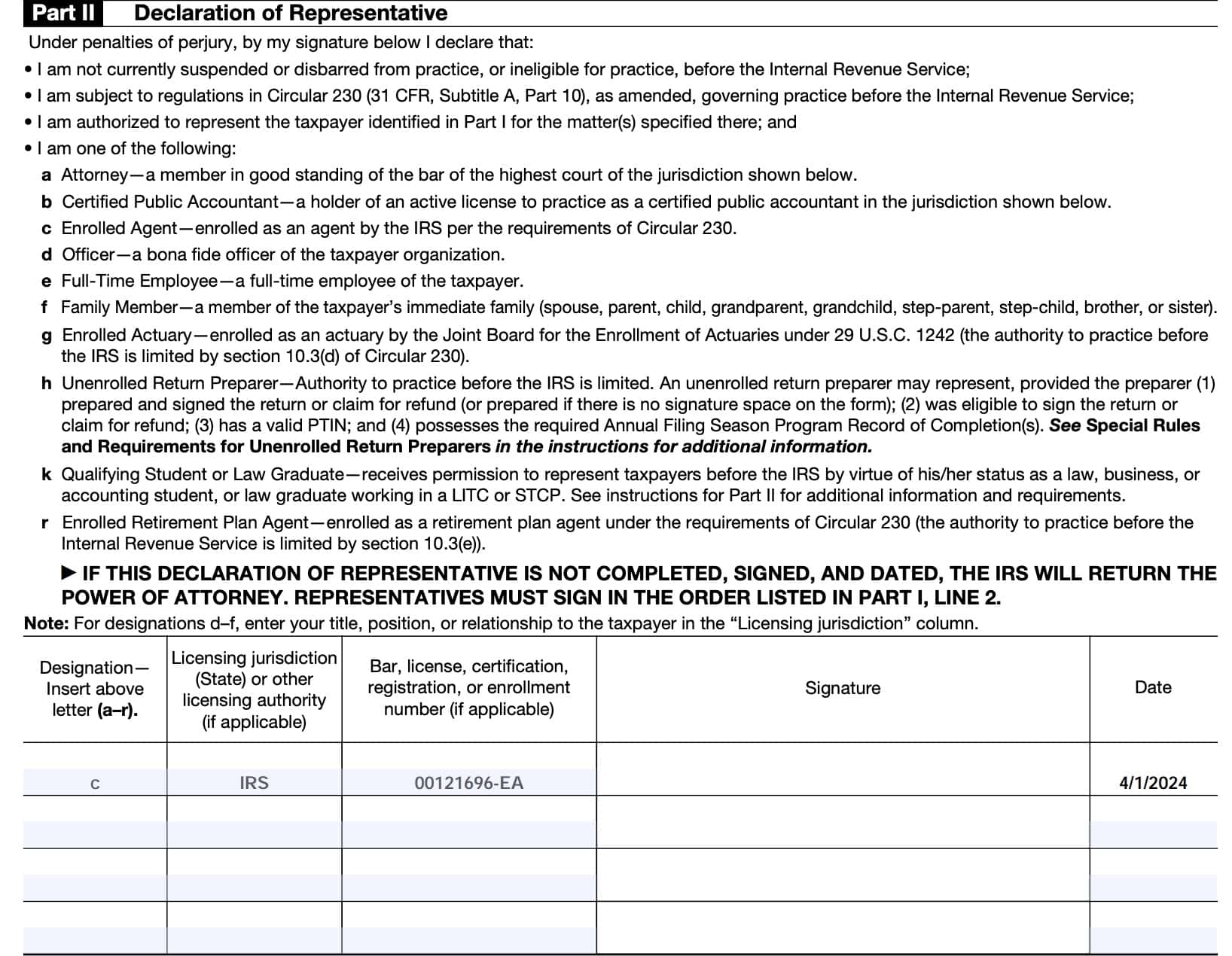
Authorized representatives
Below is a list of the authorized representatives, by designation, and what should go into the respective field:
- Attorney: Enter the two-letter abbreviation for the state in which the attorney is admitted to practice, and the associated bar or license number
- Certified public accountant: Enter the two-letter abbreviation for the state in which the CPA is licensed, and the associated certification or license number
- Enrolled agent: Enter the enrollment card number
- Officer: Enter the officer’s title within the company
- Full-time employee: Enter the employee’s title within the company
- Family member: Enter the family member’s relationship to the taxpayer. For immediate family members only, including:
- Spouse
- Parent
- Child
- Sibling
- Grandparent or grandchild
- Step-parent, step-child, step-brother, or step-sister
- Enrolled actuary: enrolled as an actuary by the Joint Board for the Enrollment of Actuaries under 29 U.S.C. 1242 (the authority to practice before the IRS is limited by section 10.3(d) of Circular 230)
- Unenrolled return preparer: Limited authority to practice before the IRS
Qualifying student or law graduate
A qualifying student or law graduate may receives permission to represent taxpayers before the IRS by virtue of his/her status as a law, business, or accounting student, or law graduate working in a low-income tax clinic (LITC) or student tax clinic program (STCP).
To select this, enter designation ‘k’ and either:
- LITC, or
- STCP
Enrolled retirement plan agent
An enrolled retirement plan agent may select designation letter ‘r’ and enter the enrollment card number that was issued by the return preparer office.
If your tax return preparer files a paper tax return on your behalf, he or she should include your completed Form 2848 with your tax return. If your preparer e-files your return, then they should submit your form with IRS Form 8453, U.S. Individual Income Tax Transmittal for an IRS e-file Return.
Video walkthrough
This instructional video walks you through IRS Form 2848, step by step.
Filing considerations
There are some filing considerations you may want to know when filing IRS Form 2848. Let’s begin by going over how to file.
How do I file IRS Form 2848?
Taxpayers may file IRS Form 2848 in one of three ways:
- Online
- Fax
Filing online
Taxpayers may file online through the Form 2848 & Form 8821 page on the IRS website. Online submissions may use electronic signatures or a digitized image of a handwritten signature.
Electronic signatures
Electronic signatures appear in many forms. The Internal Revenue Service will accept the following electronic signature methods:
- A typed name that is typed into the signature block;
- A scanned or digitized image of a handwritten signature that is attached to an electronic record;
- A handwritten signature input onto an electronic signature pad;
- A handwritten signature, mark, or command input on a display screen with a stylus device; or
- A signature created using third-party software.
If the taxpayer electronically signs Form 2848 in a remote transaction, the third party submitting Form 2848 to the IRS on behalf of the taxpayer must attest that he or she has authenticated the taxpayer’s identity.
A remote transaction for an electronic signature occurs when the taxpayer is electronically signing the form and the third-party submitter isn’t physically present with the taxpayer.
Filing by fax or mail
If you wish to file by fax or mail, then you should send your completed Form 2848 to the IRS address or fax number that corresponds to where you live.

Who is authorized to practice in front of the IRS?
According to the IRS instructions, these individuals are authorized to practice before the IRS, as well as specific requirements for each type of representative.
Attorney
The attorney must be a member in good standing of the bar of the highest court in the jurisdiction described in Part II of the form. Although any attorney can meet this criteria, this usually would be a tax attorney.
Certified Public Accountant
A certified public accountant (CPA) must hold an active license to practice as a CPA in the jurisdiction outlined in Part II of this form.
Enrolled Agent
An enrolled agent is a person authorized to practice before the IRS per the requirements outlined in Circular 230.
Officer
Must be a bona fide officer of the taxpayer organization he or she is representing.
Full-time employee
Must be a full-time employee of the taxpayer.
Family member
Must be a member of the taxpayer’s immediate family. This includes the following family members:
- Spouse
- Parent
- Child
- Grandparent
- Grandchild
- Step-parent
- Step-child
- Sibling
Enrolled actuary
Must be enrolled as an actuary by the Joint Board for the Enrollment of Actuaries under 29 U.S.C. 1242. This authority to practice before the IRS is limited to certain areas of the tax code by Section 10.3(d) of Circular 230).
Unenrolled tax return preparer
An unenrolled tax return preparer has limited authority to practice before the IRS. An unenrolled return preparer may represent in the following situations:
- The preparer prepared and signed the tax return or claim for refund, or at least prepared the form if there is no signature space
- The preparer was eligible to sign
- The preparer has a valid preparer tax identification number (PTIN)
- The tax preparer has the required Annual Filing Season Program Record of Completion.
There is more specific information in the Special Rules and Requirements for Unenrolled Return Preparers section of the tax form instructions.
Qualifying student or law school graduate
A qualifying student or law graduate receives permission to represent taxpayers before the IRS by virtue of his/her status as a law, business, or accounting student, or law graduate working in a low income taxpayer clinic (LITC) or student tax clinic program (STCP).
However, that student or graduate must name their lead attorney or CPA first, then themselves on the next line of the Form 2848.
Enrolled retirement plan agent
Must be enrolled as a retirement plan agent under the requirements of Circular 230. This authority to practice before the IRS is limited to certain areas of the tax code by Section 10.3(e) of Circular 230.
Representative responsibilities
All representatives must declare, under penalty of perjury, the following:
- I am not currently suspended or disbarred from practice, or ineligible for practice, before the IRS
- I am subject to regulations in Circular 230 (31 CFR, Subtitle A, Part 10), as amended, governing practice before the Internal Revenue Service
- I am authorized to represent the taxpayer identified in Part I for the matter(s) specified there
Generally speaking, all attorneys, CPAs, enrolled agents, enrolled actuaries, and enrolled retirement plan agents are considered tax professionals or tax practitioners.
What your representative can do for you
By completing IRS Form 2848, a taxpayer acknowledges that their qualified representative will be able to receive and inspect the taxpayer’s confidential information.
Taxpayers can file Form 2848, if the IRS begins a Foreign Bank and Financial Accounts (FBAR) examination as a result of an income tax examination. The Representation for FBAR Issues Section of Report of Foreign Bank and Financial Accounts (FBAR) contains more complete information on this topic.
Frequently asked questions
A taxpayer may use IRS Form 2848 to authorize an individual to represent that taxpayer in federal tax matters before the IRS. However, the individual must be eligible to practice before the IRS, as outlined in Part II of this form.
You may revoke an existing 2848 form by filing a new Form 2848. If you select a new representative, you simply do not check the box on Line 6. If you do not add a new power of attorney, you may write ‘REVOKE’ across the top, then sign and date the form.
Yes. The IRS will accept a Form 2848 with either an electronic signature or a digitized image of a handwritten signature submitted through the IRS website.
No. But your power of attorney must meet the requirements outlined in IRS Publication 216, Conference and Practice Requirements, and 26 CFR 601.503(a). Additionally, Form 2848 must accompany the form if you wish it to be recorded in the CAF.
Where can I find a copy of IRS Form 2848?
You may download the latest version of this tax form from the IRS website or by selecting the file below.